Explain Various Types of Computers?
https://www.computersprofessor.com/2016/04/various-types-of-computers.html
|
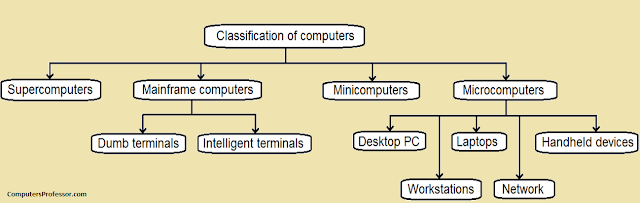
Classification
of Computers
|
|
Computers
can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount
of data that they can hold, and price (refer to figure). These categories are
as follows :
·
Supercomputers
·
Mainframe
computers
·
Minicomputers
·
Microcomputers
|
|
Supercomputers
|
|
Among
the four categories, the supercomputer is the fastest, most powerful, and
most expensive computer. Supercomputers were first developed in the 1980s to
process large amounts of data and to solve complex scientific problems.
Supercomputers use parallel processing technology and can perform more than
one trillion calculations in a second.
A
single supercomputer can support thousands of users at the same time. Such
computers are mainly used for weather forecasting, nuclear energy research,
aircraft design, automotive design, online banking, controlling industrial
units, etc.
|
|
Mainframe
Computers
|
|
Mainframe
computers are large–scale computers (but smaller than supercomputers). These
are very expensive and need a very large clean room with air conditioning,
thereby making them very costly to deploy. As with supercomputers, mainframes
can also support multiple processors. Users can access mainframes by either
using terminals or via PCs. There are basically two types of terminals that
can be used with mainframe systems that are discussed as follows :
Dumb
Terminals
Dumb terminals consist of only a
monitor and a keyboard (or mouse). They do not have their own CPU and memory
and use the mainframe system’s CPU and storage devices.
Intelligent
Terminals
In contrast to dumb terminals,
intelligent terminals have their own processor and thus can perform some
processing operations. However, just like the dumb terminals, they do not
have their own storage space. Usually, PCs can be used as intelligent
terminals to facilitate data access and other services from the mainframe
system.
Mainframe
computers are typically used as servers on the world wide web. They are also
used in large organizations such as banks, airline companies and
universities, where a large number of users frequently access data stored in
their databases.
|
|
Minicomputers
|
|
As
the name suggests, minicomputers are smaller, cheaper, and slower than
mainframes. They are called minicomputers because they were the smallest
computer of their times. Also known as midrange computers, the capabilities
of minicomputers fall between mainframe and PCs.
Minicomputers
are widely used in business, education, hospitals, government organizations,
etc. While some minicomputers can be used only by a single user, others are
specifically designed to handle multiple users simultaneously. Usually,
single–user minicomputers are used for performing complex design tasks.
As
with mainframes, minicomputers can also be used as servers in a networked
environment, and hundreds of PCs can be connected to it.
|
|
Microcomputers
|
|
Microcomputers,
commonly known as PCs, are very small and cheap. PCs can be classified into
the following categories :
Desktop
PCs
A
desktop PC is the most popular model of PCs. The system unit of the desktop PC
can be placed flat on a desk or table. It is widely used in homes and
offices.
Laptops
Laptops
are small microcomputers that can easily fit inside a briefcase. They are
very handy and can easily be carried from one place to another. They may also
be placed on the user’s lap (thus the name). Hence, laptops are very useful,
especially when going on long journeys. Laptops operate on a special battery
and do not always have to be plugged in like desktop computers.
The
memory and storage capacity of a laptops is almost equivalent to that of a
desktop computer. As with desktop computers, laptops also have HDDs, floppy
disk drivers, zip disk drives, etc. For input, laptops have a built–in
keyboard and a trackball/touchpad, which is used as a pointing device.
Workstations
Workstations are single-user computers that have the
same features as PCs, but their processing speed matches that of a
minicomputer or mainframe computer. Workstation computers have advanced
processors, more RAM and storage capacity than PCs. Therefore, they are more
expensive and powerful than a normal desktop computer.
Network
Computers
Network
computers have less processing power, memory, and storage than a desktop
computer. These are specially designed to be used as terminals in a networked
environment. For example, some network computers are specifically designed to
access data stored on a network (including the Internal and intranet).
Some
network computers do not have any storage space and merely rely on the
network’s server for data storage and processing tasks.
Network
computers that are specifically designed to access only the Internet or
intranet are often known as Internet PCs or Internet boxes.
Handheld
Computers
The mid 1990s witnessed a range of small personal
computing devices that are commonly known as handheld computers, Palmtop
computers, or Mini–Notebook computers. These computers are called handheld
computers because they can fit in one hand, while users can use the other
hand to operate them. Handheld computers are very small in size, and hence
they have small-sized screens and keyboards. Some examples of handheld
computers are
·
Personal
digital assistant (PDA)
·
Cellular
telephones
·
H
/ PC Pro devices.
Personal
digit assistants (PDA) :
Today,
the PDA (shown in figure) is among the most popular lightweight mobile
devices that are used. A number of PDAs available in the market offer a
collection of application software for word processing, spreadsheets, games,
etc. PDAs are used to take notes, organize telephone numbers, and store
addresses.
The
primary input device of a PDA is the stylus. A stylus enables the user to
interact with the touchscreen to write text or drawn figures. It can be used
to write notes. Some PDAs also support voice input.
Cellular
phones :
These
days, cellular phones are web enabled telephones that have features of both
analogue and digital devices. Such phones are also known as smart phones
because, in addition to basic phone capabilities, they also facilitate the users to access the
Internet and send e-mails and faxes.
H
/ PC Pro devices :
The
H / PC Pro device see figure is based on a new development in handheld
technology. The size and features of the H/PC Pro device is more than PDAs
but less than that of typical notebook PCs. The H/PC Pro device includes a
full-sized keyboard, RAM with very low storage capacity, and a slow-speed
processor. However, these devices do not have a secondary storage disk.
|